Every society depends on fairness, and the law plays an important role in protecting that balance.
In the United States, equality under the law means no one should be treated unfairly because of personal traits they cannot change.
To make this principle real, lawmakers have defined certain groups that must be protected from discrimination.
These protections don’t offer special treatment, but they ensure a level playing field where everyone has the same opportunity to work, live, and participate freely.
Knowing why legislation identifies protected classes explains how the legal system works to prevent discrimination and promote justice.
What Are Protected Classes?
A protected class definition in U.S. law refers to groups of people who share certain characteristics and receive legal protection from discrimination.
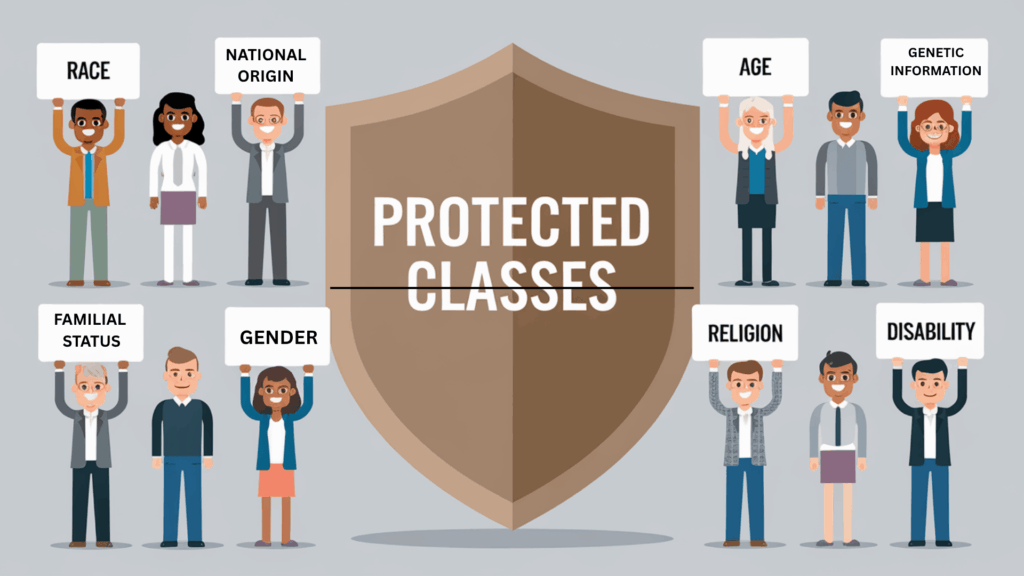
Federal civil rights laws recognise several key traits that cannot be used as grounds for unfair treatment.
Federally Recognised Protected Classes:
These are groups specifically identified by U.S. law as needing protection from discrimination.
They form the foundation of anti-discrimination policies across employment, housing, and public services.
Under federal law, the following characteristics are protected:
- Race and Colour
- Religion
- Sex
- National Origin
- Age
- Disability
- Genetic Information
These protections ensure that individuals are treated fairly and not denied opportunities based on personal traits.
Also Read: Law Firm Hierarchy: Roles and Career Paths
Why Does Legislation Identify Protected Classes?
The reasons why laws identify protected classes include constitutional foundations, addressing past discrimination, and ensuring fair enforcement.
By defining specific groups, lawmakers create enforceable rights that prevent discrimination in daily life.
These laws serve three main purposes:
- Constitutional foundation: They uphold the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment.
- Historical correction: They address long-standing patterns of inequality and exclusion.
- Practical enforcement: They establish clear standards for courts and employers to follow.
In simple terms, these legal categories exist to make equality measurable, enforceable, and consistent across the nation.
Why Does Legislation Identify Protected Class Civil Rights?
The idea of protected classes in legislation originates from America’s civil rights movement, when lawmakers recognized that fairness requires enforceable legal protections.
The Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment is the core of this effort.
It requires every state to treat individuals equally under the law, setting the stage for modern civil rights protections.
Over time, Congress passed major legislation to turn this principle into action:
- Civil Rights Act of 1964: Prohibited discrimination in employment and public accommodations. It also opened the door to broader protections in education and voting rights.
- Fair Housing Act of 1968: Banned housing discrimination. It ensured equal access to buying, renting, and financing homes.
- Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990: Protected people with disabilities. It required public spaces and workplaces to provide reasonable accommodations.
- Age Discrimination in Employment Act: Protected older workers. It prevented unfair treatment in hiring, promotions, and job benefits.
These laws show why legislation identifies protected classes, aiming to provide all people with equality under the law, fair opportunity, and legal support against discrimination.
How State Laws Expand Protected Class Rights?
Federal law provides the basic framework for anti-discrimination protections, but many states go further by recognizing additional protected classes.
These state laws address local needs and ensure broader protection against unfair treatment.
Common additional protected class categories include:
- Sexual orientation
- Gender identity
- Marital status
- Military service
- Political beliefs
States such as California, New York, and Massachusetts have some of the most comprehensive civil rights protections in the nation.
They extend safeguards across employment, housing, education, and public services, ensuring equal access and opportunity for all.
Because these protections vary from state to state, individuals should be aware of both federal and state laws that apply to them.
What Are Examples of Discrimination Against Protected Classes?
Discrimination against protected classes can appear in many forms across daily life.
It may involve being denied a job, promotion, or housing opportunity because of race, gender, age, or disability.
In workplaces, this can include unfair pay, exclusion from training or advancement, or being targeted with offensive remarks or harassment.
In education, discrimination may show up as biased admissions decisions, unequal disciplinary actions, or a lack of accommodations for students with disabilities.
In housing or public services, it can include landlords refusing to rent or businesses denying access based on protected traits.
All these actions violate civil rights laws and can lead to complaints, investigations, or legal penalties.
What Should You Do If You’ve Faced Discrimination?
If you believe you’ve been discriminated against, you have several legal options to protect your rights and seek justice.
Start by documenting what happened, including dates, people involved, and any communication or evidence.
You can then file a complaint with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) or your state’s fair employment agency.
These organizations investigate discrimination claims and can help resolve issues through mediation or legal action.
It’s also wise to consult an employment or civil rights attorney for guidance on your specific situation.
When you understand why legislation identifies protected classes, it’s easier to recognize discrimination and take the right steps to address it.
Read more: How to Identify and Handle FMLA Violations?
Social and Legal Implications

Protected class laws benefit both individuals and society.
They protect people from unfair treatment and help create a fairer, more inclusive nation.
Individual Protections
Protected class status provides meaningful benefits across daily life.
It also gives individuals the right to take legal action when their rights are violated.
- Employment: Workers cannot be fired, denied promotion, or treated unfairly because of protected characteristics.
- Housing: Landlords cannot refuse to rent or sell based on protected status.
- Education: Schools must provide equal access regardless of protected traits.
- Public Services: Government services and public accommodations must be available to everyone.
Societal Benefits
These laws create broader social advantage.
They promote fairness, inclusion, and equal opportunities within communities.
- Economic Growth: When all people can participate fully in economic life, the entire economy benefits from increased productivity and innovation.
- Social Stability: Fair treatment reduces social tension and promotes national unity.
- International Standing: Strong civil rights laws enhance America’s reputation as a leader in human rights.
The Changing Scope of Protection
Protected class categories continue to evolve as society and technology advance.
Recent updates include expanded protections, new legal rulings, and emerging issues that reflect modern challenges.
LGBTQ+ Rights: Many states now include sexual orientation and gender identity, and the Bostock v. Clayton County (2020) ruling extended federal workplace protections to LGBTQ+ employees.
Emerging Issues: Future protections may cover genetic discrimination and bias linked to medical conditions.
Technology Challenges: The rise of algorithmic bias and online harassment highlights the need for updated laws to address digital-age discrimination.
Looking for more content like this?
Read our next article for deeper insight. Americans with Disabilities Act Attorney
Conclusion
Protected classes exist because history has shown that without clear legal protections, discrimination thrives.
By naming specific groups, lawmakers created enforceable rights, corrected injustices, and built a fairer society.
These laws are not only about individual protections; they strengthen communities, foster equality, and keep opportunities open to everyone.
Knowing your rights under these laws empowers you to recognise discrimination and respond effectively.
Comment below and share your stories to inspire others.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does Being Part of a Protected Class Mean?
It means you’re legally protected from discrimination based on traits like race, religion, sex, age, or disability. These protections give you the right to challenge unfair treatment through legal channels.
Which Classes Are Protected by Federal Law?
Federal law protects race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age (40+), disability, and genetic information. These categories set the minimum standard of protection across the country.
Can States Add More Protected Classes?
Yes, states can and often do provide broader protections than federal law. This means your rights may vary depending on where you live or work.
Why Do Some Groups Qualify for Protection While Others Do Not?
Groups usually qualify when there’s a history of unfair treatment and a need for legal remedies. Lawmakers assess documented patterns of discrimination before granting protection.