A well-functioning workplace depends on the crucial factor of everyone knowing what to do with clear expectations.
When people understand their responsibilities, productivity tends to increase, and confusion decreases.
This resource walks you through creating effective role descriptions, complete with practical examples.
By the end, you should have practical tools for writing workplace documentation that works for your organization.
What Is A Role Description And Why Does It Matter?
A role description helps establish clear boundaries, set performance standards, and show employees how their work contributes to company goals.
Think of it as a roadmap that outlines what someone might accomplish on a daily basis.
For employers, these documents can provide a foundation for performance reviews and hiring decisions.
Role descriptions often improve recruitment by attracting suitable candidates and reducing mismatched expectations.
During job applications, candidates encounter role descriptions as a preview of daily responsibilities to help assess if the position aligns with their goals.
Role Description vs. Job Description
Role descriptions are actually a key component within position outlines, not separate documents.
| Basis of Difference | Role Description | Job Description |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Daily tasks and responsibilities | Complete position overview |
| Content Scope | Specific duties for current role | Qualifications, benefits, and requirements |
| Key Question Answered | “What will you do?” | “What does this opportunity offer?” |
| Main Purpose | Performance management | Recruitment and hiring |
| Target Audience | Current employees | Potential candidates |
Both documents work together to provide complete information about a position.
Well-written role descriptions not only help employers but can also help candidates prepare better for interviews.
How to Write Role Responsibilities for a Job Description?

Role responsibilities outline what an employee is expected to do in their position, helping both the employer and candidate set clear expectations.
When writing them, aim for clarity, action, and alignment with organizational goals.
Here are key steps to follow:
1. Start with Action-Oriented Language
Begin each responsibility with a strong action verb such as manage, coordinate, design, analyze, or support.
This makes the duties sound active and measurable, helping candidates immediately grasp what they will be doing rather than reading vague or passive statements.
2. Be Specific but Concise
Write responsibilities that give enough detail to convey the exact task without overwhelming the reader.
For example, instead of “handles communication,” use “manages client communication through emails, presentations, and scheduled meetings.” This approach balances clarity with brevity.
3. Prioritize Core Responsibilities
Place the most critical and frequently performed duties at the top of the list.
This ensures candidates quickly recognize the primary focus of the role and understand which tasks will define their daily performance and long-term contributions.
4. Keep Them Outcome-Focused
Link responsibilities to results to show their purpose.
For instance, “develops social media campaigns to increase brand engagement” not only explains the activity but also shows how the role supports company objectives, giving candidates a sense of impact.
5. Use Bullet Points for Readability
Structure responsibilities as bullet points rather than long paragraphs.
Aim for 5–7 points that capture the most important duties.
A bulleted list is easier for candidates to scan and helps maintain a clear, organized job description.
6. Avoid Jargon or Vague Terms
Refrain from using unclear or overly broad statements like “handles tasks as needed.”
Instead, specify duties, such as “prepares monthly financial reports for leadership review,” ensuring that applicants know exactly what will be expected from them.
7. Reflect Collaboration and Scope
Clarify how the role interacts with others and the level of authority it carries.
For example, mention if the position supervises a team, collaborates with external partners, or provides support to senior leadership, ensuring expectations are transparent.
Sample Job Description
This sample shows you exactly how to format a complete position outline with all the essential sections.
The role description works alongside qualifications and working conditions to create a comprehensive overview.

Download these and more examples in a PDF format to make your own job description.
Elements That Make Role Descriptions Effective
Writing effective role descriptions requires focusing on key components that bring clarity and set expectations:
- Clear Responsibility Definitions: Use action verbs like develop, schedule, or manage to define tasks and set performance expectations.
- Collaboration Requirements: Highlight teamwork with phrases like coordinate with or support sales team to show cross-departmental involvement.
- Qualification Standards: Specify education and experience (e.g., Bachelor’s degree, 2–3 years) to filter applicants realistically.
- Technical Competencies: List tools or skills such as Python, SQL, Google Analytics, or social media platforms to set clear benchmarks.
- Working Conditions: Mention details like office environment, occasional travel, or 10% overtime to give a practical view of the role.
Benefits of Defining Role-Specific Responsibilities
Clearly defining role-specific responsibilities in a job description provides numerous advantages for both organizations and employees.
Here are five key benefits:
- Enhances Clarity: Employees understand expectations and responsibilities clearly.
- Improves Hiring Accuracy: Attracts qualified candidates and reduces mismatches.
- Supports Performance Management: Makes tracking and evaluating performance easier.
- Reduces Overlap: Prevents task duplication and team conflicts.
- Facilitates Career Growth: Helps employees plan development and advancement opportunities.
Job Description Templates Category Wise
Below are few practical templates for PR, Events, Brand Management, and Business Analysis roles with complete frameworks:
1. Public Relations
|
Job Title: Public Relations Specialist Department: Marketing / Communications Reports To: PR Manager / Head of Communications Role OverviewThe Public Relations Specialist is responsible for managing the company’s image, building positive relationships with the public, and handling media communications. This role involves creating press materials, coordinating campaigns, and supporting brand reputation. Key Responsibilities
Qualifications
Skills and Competencies
Working Conditions
|
2. Event Coordinator
Role OverviewAn Event Coordinator is responsible for planning, organizing, and executing events that align with organizational objectives. This role ensures smooth logistics, effective communication with stakeholders, and a positive experience for attendees. Key Responsibilities
Qualifications
Skills and Competencies
Working Conditions
|
3. Brand Manager Role Description
Role OverviewA Brand Manager is responsible for developing and maintaining a company’s brand identity, ensuring consistency across all marketing channels, and driving strategies that strengthen brand recognition and customer loyalty. This role combines creativity, analysis, and leadership to support overall business growth. Key Responsibilities
Qualifications
Skills and Competencies
Working Conditions
|
4. Business Analyst
Role OverviewA Business Analyst acts as the link between stakeholders and technical teams, identifying business needs, analyzing processes, and recommending solutions that improve efficiency and support organizational goals. The role focuses on gathering requirements, data-driven decision-making, and ensuring smooth project delivery. Key Responsibilities
Qualifications
Skills and Competencies
Working Conditions
|
Job Description Examples
Here are Three Comprehensive Examples that Demonstrate Effective Workplace Documentation Across Different Industries:
1. Data Scientist

2. Software Engineer

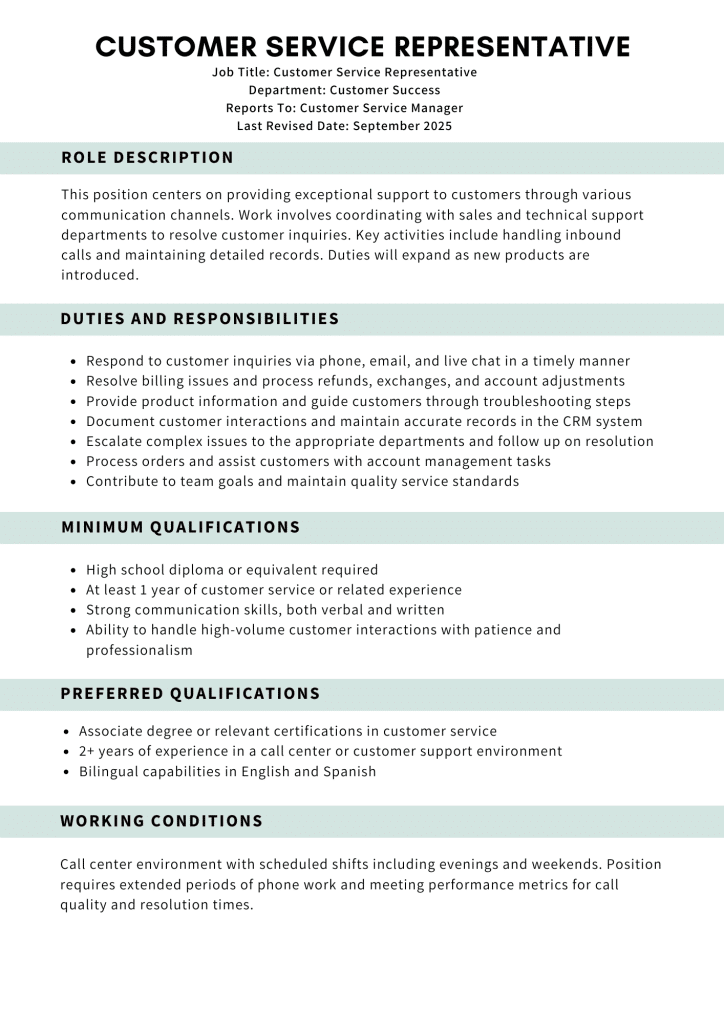
3. Customer Service Representative
Dos And Don’ts For Employment Postings
Writing Effective Workplace Documentation Follows Proven Guidelines While Avoiding Common Mistakes.
These Guidelines Ensure Your Position Outlines Attract the Right Candidates and Set Clear Expectations, without Leaving Room for Confusion.
| Basis of Difference | Do | Don’t |
|---|---|---|
| Language and Clarity | Use Clear, Specific Language with Action Verbs | Use Vague Terms Like “various Duties” or Industry Jargon |
| Qualification Standards | List Essential Requirements Separately from Preferred Ones | Include Unrealistic Qualifications that Eliminate Good Candidates |
| Responsibility Details | Focus on Key Duties that Define the Role’s Success | List Every Possible Task or Create Overwhelming Bullet Points |
| Company Information | Include Relevant Culture and Growth Opportunities | Oversell the Position or Omit Less Appealing Aspects |
| Legal Compliance | Ensure All Requirements Relate Directly to Job Performance and Comply with Employment Law | Include Discriminatory Language or Irrelevant Personal Preferences |
Conclusion
Effective Position Outlines can Serve as a Helpful Foundation for Successful Hiring and Employee Performance Management.
They May Help Bridge the Gap Between Organizational Needs and Candidate Expectations, Potentially Reducing Turnover and Improving Job Satisfaction.
Remember that These Documents Evolve with Your Business and Should be Reviewed Regularly, Especially when Job Duties Change Significantly or Annually.
Learning the Role Description and Its Application can Improve Hiring Outcomes and Employee Clarity.
Investing Time in Well-Crafted Descriptions Often Pays Off Through Better Candidate Quality.
Consider Implementing These Frameworks to Improve Your Hiring Process.
Have thoughts or experiences with creating effective position outlines? Share your insights in the comments below!