Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) protect sensitive business information from unauthorized sharing.
Companies rely on these legal contracts to safeguard trade secrets, client data, and confidential details.
But what happens if you break an NDA? The consequences can be serious and costly.
Violating these agreements may result in lawsuits, financial penalties, and professional reputation damage.
It covers the legal, financial, and career impacts of NDA violations.
You’ll learn about potential penalties, when breaches become criminal matters, and how to avoid costly mistakes with confidential information.
Understanding Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs)
An NDA is a legal contract that prevents people from sharing confidential information.
These agreements protect trade secrets, business strategies, and sensitive data from being disclosed to unauthorized parties.
NDAs are commonly used in employment contracts, business partnerships, and vendor agreements to maintain competitive advantages.
Most NDAs include specific terms about what information must remain private and the duration of the agreement.
How NDAs Function and What They Cover?
NDAs function by creating legal obligations between parties to keep specific information secret.
These contracts outline what information must remain confidential and the duration of the agreement.
Types of NDAs
- Unilateral NDA – Only one party shares confidential information
- Bilateral NDA – Both parties exchange sensitive information
- Multilateral NDA – Three or more parties share confidential details
Core components include confidential information definitions, obligations of each party, time limits, and penalties for violations.
Courts determine enforceability based on clear language, reasonable terms, and legitimate business interests.
What Happens if You Break an NDA?
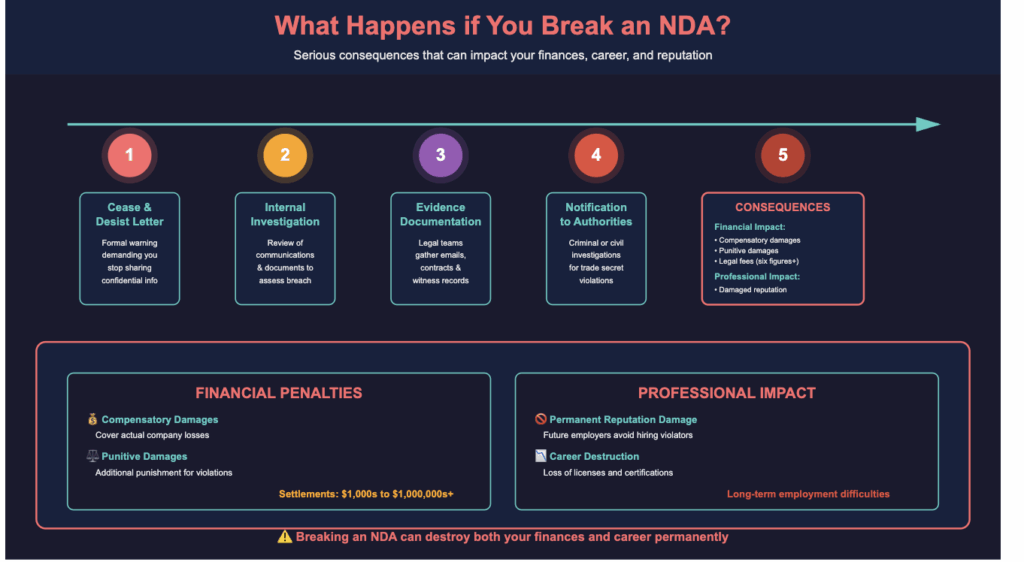
Breaking an NDA can have serious consequences, potentially affecting your finances, career, and professional reputation.
Companies respond quickly to protect confidential information and may take legal action against violators.
1. Cease and Desist Letters
The first step is often a formal cease and desist letter, demanding that you immediately stop sharing or using the confidential information.
This letter serves as an official warning and can be used as evidence if the matter escalates to court.
2. Internal Investigation
Companies typically launch an internal investigation to determine the extent of the breach.
This includes reviewing communications, documents, and other evidence to assess how much confidential information was disclosed and to whom.
Employees under investigation for NDA breaches may be placed on administrative leave; learn what administrative leave means and how it works.
3. Evidence Documentation
Legal teams carefully document all relevant evidence to prepare for potential lawsuits.
This documentation may include emails, contracts, witness statements, and records of any actions you took that violated the NDA.
4. Notification to Authorities
If the breach involves trade secrets or sensitive proprietary information, authorities may be notified.
This can lead to criminal investigations or civil actions under laws like the Economic Espionage Act or the Defend Trade Secrets Act, depending on the severity of the violation.
5. Financial and Professional Impact
Financial penalties include compensatory damages for actual losses, punitive damages as punishment, and legal fees often reaching six figures.
Settlement amounts range from thousands to millions, depending on case severity. These costs can destroy personal finances and create long-term debt.
Professional consequences are equally damaging. Your reputation suffers permanent harm, making future employment difficult.
Companies avoid hiring people with confidentiality violations, and you may lose professional licenses or certifications.
If a violation leads to job loss, it helps to know the difference between being laid off and terminated.
Legal Repercussions:
| Legal Action | Description | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Civil Lawsuit | Court action seeking monetary damages | Financial compensation orders |
| Injunctive Relief | Court order to stop further disclosures | Legal ban on sharing information |
| Asset Seizure | Removal of materials containing confidential data | Loss of documents, devices, files |
| Discovery Process | Forced disclosure of communications and records | Privacy invasion, evidence gathering |
How to Avoid Breaking an NDA?
To prevent violating an NDA, handle all confidential information carefully and share it only with authorized individuals.
Understand the agreement’s terms, including what information is protected and the duration of confidentiality.
Keep organized records of communications and documents related to sensitive material.
Avoid discussing confidential matters in public or online.
If uncertain about sharing any information, consult a legal professional before taking action.
Staying aware of your responsibilities and acting cautiously helps protect your professional reputation and prevents costly legal and financial consequences.
If your employer plans disciplinary action for an NDA issue, you might receive a pre-adverse action notice; see what it means and how it works.
Penalties for Violating an NDA
NDA violations result in civil penalties through the court system.
Most breaches are handled as contract disputes rather than criminal matters, but serious cases can cross into criminal territory.
1. Civil Penalties: Civil courts award monetary damages to cover actual business losses and legal fees for both parties, often totaling hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Courts issue injunctions preventing further information sharing and may seize assets containing confidential data.
2. Criminal Charges: Criminal liability occurs in severe cases involving theft of trade secrets, fraud, or espionage.
Government agencies prosecute violations related to national security or major corporate espionage, resulting in fines and imprisonment.
3. Factors Affecting Penalties: Penalty severity depends on breach severity, actual harm caused, and NDA enforceability. Intentional violations receive harsher punishment than accidents.
How Long Does an NDA Last?
NDA duration varies depending on the specific terms written into your agreement. Understanding these time limits is crucial because your obligations continue for the entire specified period.
Fixed-Term vs. Indefinite NDAs:
| Fixed-Term NDAs | Indefinite NDAs |
|---|---|
| Specific end dates (1-5 years typical) | Last until information becomes public |
| Tied to employment periods | Protect trade secrets permanently |
| Based on the last access to information | Continue indefinitely for valuable data |
| Easier court enforcement | Subject to reasonableness tests |
Duration Clause Importance: Reasonable time limits increase court enforcement chances, while excessive terms may be ruled unenforceable.
Courts balance legitimate business interests against your right to work freely. Some states limit NDA duration through laws protecting employee mobility.
How to Get Out of an NDA?
Getting out of an NDA legally requires specific circumstances or proper procedures.
Attempting to exit improperly leads to the same consequences as violations, making it important to know what happens if you break an NDA before taking action.
Legal Ways to Terminate an NDA
- Mutual consent – Both parties agree to end the agreement in writing
- Natural expiration – The NDA reaches its specified end date
- Fraud or duress – You signed under false pretenses or pressure
- Information becomes public – Confidential data loses its protected status through other sources
- Court invalidation – A judge rules the NDA unenforceable due to unreasonable terms
Risks of Unilateral Termination: Attempting to break an NDA without legal grounds exposes you to the same penalties as standard violations.
Companies will pursue full legal remedies, including damages, injunctions, and legal fees. If you believe the NDA is invalid, courts must make that determination.
Recommended Approach: Consult with a contract attorney before attempting to exit any NDA.
Legal professionals can evaluate your specific situation and determine if legitimate grounds exist for termination.
For more detailed information on legal rights and employer obligations, head to our Legal Framework page. It covers everything from confidentiality laws to employee protections.
Conclusion
What happens if you break an NDA is essential for protecting your career and finances.
The consequences include costly lawsuits, substantial damages, and permanent reputation damage that can last for years.
Financial penalties often reach hundreds of thousands of dollars, while criminal charges apply in severe trade secret cases.
Before signing any NDA, carefully review the terms and consult with a qualified attorney if facing potential violations.
Have you dealt with NDA issues in your career?
Share your experiences in the comments below.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Does an NDA Cost?
Basic NDAs cost $200-$500 with an attorney or $50-$100 for online templates. Complex agreements can reach $1,000-$3,000 depending on industry requirements.
Is an NDA a Big Deal?
Yes, NDAs are legally binding contracts with serious consequences. Violations result in expensive lawsuits, financial damages, and permanent career damage.
Can an NDA Be Used Against You?
NDAs can be used against you for violating confidentiality terms. However, they cannot prevent you from reporting illegal activities or workplace harassment