Our world grows more connected each day.
People from different countries, backgrounds, and cultures work together, study together, and live in the same communities.
This mixing of cultures creates both opportunities and challenges in how we talk and connect with each other.
Intercultural communication helps us bridge these cultural gaps.
It teaches us how to share ideas, build relationships, and work together despite our different backgrounds and ways of thinking.
In this post, I will cover everything you need to know about intercultural communication.
What is Intercultural Communication?
The definition of Intercultural communication is the process of sharing information and ideas between people from different cultural backgrounds.
It happens when individuals with different values, beliefs, languages, and social practices try to understand each other.
This goes beyond language.
Culture affects communication styles, decision-making, and social interactions in every setting.
Intercultural Communication Examples
1. American doctors speak directly about health issues, while some Asian cultures prefer family-centered communication.
2. German workers favor detailed plans, Brazilians prefer face-to-face discussion. These differences appear in healthcare, workplaces, and schools daily.
3. In U.S. classrooms, students are encouraged to ask questions openly, whereas in many East Asian cultures, silence shows respect for teachers.
4. In European workplaces, colleagues might challenge each other’s ideas openly in meetings, while East Asian cultures prioritize harmony and avoid confrontation.
5. Scandinavians expect a flat structure, while Latin Americans respect hierarchy in decision-making.
The 4 Types of Intercultural Communication
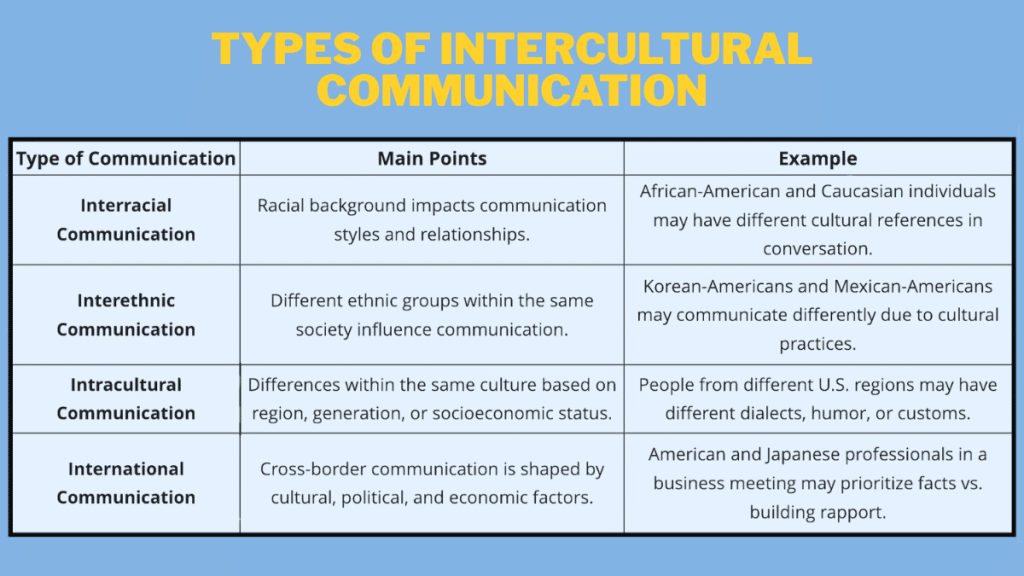
Intercultural communication takes many forms, each shaped by language, culture, and context.
From spoken words to silent gestures, and from face-to-face meetings to digital platforms, each type brings unique challenges and opportunities.
Below are the four main types that highlight how cultures interact and influence one another.
1. Interracial Communication
Interracial communication focuses on interactions between people of different racial backgrounds.
This type deals with how racial identity impacts communication styles, attitudes, and relationship-building.
In many cases, individuals from different racial groups may have distinct cultural values, social norms, and communication preferences.
These differences can create both opportunities and challenges in establishing mutual understanding and respect.
Example: A conversation between an African-American and a Caucasian person in the U.S. may involve different cultural references or experiences, influencing the way they communicate and perceive each other.
2. Interethnic Communication
Interethnic communication refers to the interactions between individuals or groups from different ethnic or cultural backgrounds who may live within the same society.
While people from the same country might share a national identity, their ethnic backgrounds often shape how they communicate, form relationships, and navigate social settings.
Interethnic communication can be particularly significant in multicultural societies, where different ethnic groups coexist and contribute to a diverse cultural landscape.
Example: Korean-Americans and Mexican-Americans living in the same city may communicate differently, shaped by their unique cultural practices, family structures, and traditions, even though they share a similar geographic location.
3. Intracultural Communication
Intracultural communication refers to interactions between individuals who share similar cultural characteristics, belonging to the same social group or co-culture.
While these individuals may come from the same broad cultural background, they may still exhibit variations based on regional, generational, or other factors within the same culture.
This type of communication is crucial for understanding the subtleties and nuances that exist even within a single culture.
Cultural differences can arise from geographic location, socioeconomic status, or personal beliefs.
Example: Two individuals from the same cultural background, but different regions of the U.S., may still experience differences in dialect, humor, and customs—showing that culture can vary even within the same group.
4. International Communication
International communication refers to communication across national borders, often involving representatives from different countries
It is the most complex form of intercultural communication.
Because it deals not only with cultural differences, it also deals with the nuances of political, economic, and social structures of different countries.
International communication often takes place in formal, professional, or diplomatic contexts, but it also extends to personal exchanges and cross-border collaborations.
Example: A business meeting between American and Japanese professionals where the American team focuses on facts and quick decisions, while the Japanese team may emphasize building rapport and understanding before finalizing any decisions.
Key Strategies of Intercultural Communication
Strategies help people connect in daily interactions, while models provide frameworks to better understand cultural differences.
Together, they make it easier to build trust, avoid misunderstandings, and work effectively with people from diverse backgrounds.
1. Active Listening
It forms the foundation of good intercultural communication.
This means focusing completely on what someone is saying and asking questions to make sure you understand correctly.
2. Open-Mindedness
This helps you approach cultural differences with curiosity rather than judgment.
Instead of thinking “that’s weird,” try thinking “that’s interesting, I wonder why they do it that way.”
3. Asking Clarifying Questions
This prevents misunderstandings from growing into bigger problems.
Simple questions like “Can you help me understand what you mean by that?” show respect and genuine interest.
4. Avoiding Stereotypes
This means treating each person as an individual rather than assuming they fit cultural generalizations.
Even people from the same culture can have very different personalities and preferences.
Interpersonal Competence vs Intercultural Strategies
Interpersonal competence in intercultural communication is the personal skillset (like empathy and adaptability) used to connect across cultures.
It’s similar to intercultural strategies, but while strategies are the actions taken, competence is the individual’s ability to apply them.
Popular Intercultural Communication Models

These models act like roadmaps, helping in understanding challenges, avoiding confusion, and improving communication across cultures.
1. Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions: This model identifies six ways cultures differ from each other.
These include power distance (how cultures handle hierarchy), individualism versus collectivism, and uncertainty avoidance (how cultures deal with unclear situations).
This model helps predict potential communication challenges.
2. Hall’s High-Context and Low-Context Cultures: This model explains how much meaning different cultures place in words versus context.
High-context cultures rely heavily on relationships, situations, and nonverbal cues.
Low-context cultures, on the other hand, communicate more directly by stating everything in words.
3. Bennett’s Developmental Model of Intercultural Sensitivity: This model describes how people gradually develop greater cultural competence.
The process begins with the denial of cultural differences and progresses toward acceptance, adaptation, and finally, integration of multiple cultural perspectives.
Why is Intercultural Communication Important?
Intercultural communication matters because it helps people work, live, and connect better across cultural differences.
It also creates environments where people feel valued and understood. Here are the importance of this communication style you should know:
1. Builds Stronger Workplace and Community Relationships
Companies with employees from many backgrounds perform better when everyone communicates well together.
Teams solve problems faster and create more innovative solutions when they combine different cultural perspectives.
Communities become more welcoming when residents understand each other’s cultural practices.
Neighbors help each other more, and conflicts happen less often.
2. Enhances Inclusivity and Reduces Conflicts
Good intercultural communication prevents many conflicts that start from cultural misunderstandings.
When people know why others act differently, they judge less and accept more.
Schools with strong intercultural communication see less bullying and more friendship between students from different backgrounds.
Workplaces experience fewer discrimination complaints and higher employee satisfaction.
3. Helps in Global Business Negotiations and Teamwork
International business deals succeed more often when negotiators understand each other’s cultural approaches.
Some cultures build personal relationships before discussing business.
Others prefer to focus on facts and numbers immediately.
Virtual teams working across countries need intercultural communication skills to meet deadlines and achieve goals.
4. Supports Personal Growth and Cultural Awareness
Learning about other cultures broadens your worldview and makes you more adaptable.
You become comfortable in new situations and are less stressed when traveling or meeting new people.
People with strong intercultural communication skills often advance faster in their careers.
Employers value workers who can connect with diverse customers and colleagues.
5. Primary Goal of Intercultural Communication
The main purpose of intercultural communication is to bridge cultural gaps and create mutual understanding between people from different backgrounds.
The goal involves promoting respect, empathy, and effective collaboration.
Another key goal is encouraging adaptability and openness to different perspectives.
This means being flexible enough to adjust your communication style when working with others, without giving up your own cultural identity.
Intercultural vs Multicultural Communication
Intercultural and multicultural communication are often used together, but they are not the same. Look at a quick comparison:
| Aspect | Intercultural Communication | Multicultural Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Interaction and exchange between people from different cultures | Coexistence of diverse cultures within the same society or group |
| Focus | Communication, relationships, and mutual understanding | Diversity, representation, and cultural presence |
| Key Idea | How cultures connect and influence each other | The existence of many cultures side by side |
| Example | A student from Japan and a student from Brazil are collaborating on a project | A city where people from many ethnic backgrounds live together |
What is an Intercultural Communication Class?
An intercultural communication class provides structured learning opportunities to practice and analyze communication across cultures.
These courses combine theory with hands-on activities to build real-world skills.
Students examine their own cultural assumptions and learn how these affect their communication style.
Classes create safe spaces to make mistakes and learn from them without serious consequences.
What do students learn? communication theories, practical models, real-life case studies, and strategy development
Conclusion
Intercultural communication is more than exchanging words. It’s about building fair, respectful, and meaningful connections.
Beyond everyday interactions, it highlights issues like power dynamics, where dominant cultures often set the tone while minority groups adapt.
Technology and media also play a growing role, shaping how cultures view each other, sometimes positively and sometimes through stereotypes.
Most importantly, it sparks personal growth by pushing us to question assumptions, adapt to new settings, and value diversity.
Start practicing these intercultural communication skills, take the first step toward building stronger relationships, and fostering a more inclusive world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Biggest Challenge in Intercultural Communication?
One of the biggest challenges is misinterpretation. The same words, gestures, or behaviors can mean different things in different cultures, which often leads to misunderstandings.
How Can Technology Improve Intercultural Communication?
Video calls, translation apps, and online collaboration tools make it easier for people from different countries to connect instantly. However, they also remove nonverbal cues, so cultural awareness is still important
Can Children Learn Intercultural Communication Skills?
Yes. Children who are exposed to diverse environments, schools, or activities can learn these skills early. This helps them grow into more open-minded and respectful adults.
How Is Intercultural Communication Used in Healthcare?
Doctors, nurses, and caregivers use intercultural communication to better understand patients’ cultural beliefs about illness, treatment, and family involvement. This builds trust and improves care.