Behavior shapes every workplace interaction, from how feedback is handled to how teams respond under pressure.
In HR settings, understanding types of behavior helps explain why employees act differently in similar situations.
Some behaviors are visible in daily actions, while others remain internal but still influence performance and decision-making.
Recognizing these patterns supports better hiring, communication, and employee management.
This article breaks down types of behavior using simple psychological explanations and practical workplace examples.
It also highlights behavior traits that fit well on a CV and explains how freshers can present them alongside skills.
The goal is to offer clear, practical insight into behavior without technical language.
Types of Behavior in Psychology
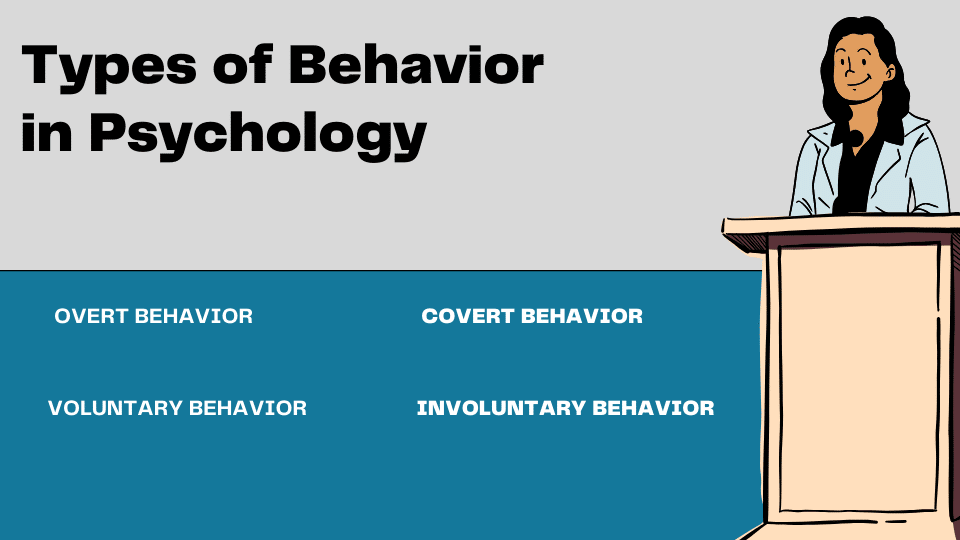
Psychology groups human actions into different types of behavior to explain how people respond to situations.
These classifications help HR professionals understand employee reactions, communication patterns, and performance under different conditions.
While psychology includes many behavior models, these four types are commonly referenced and easy to apply in workplace settings.
1. Overt Behavior
Overt behavior includes actions that can be seen or heard by others.
This type of behavior is visible and measurable, making it easier to observe and assess in a workplace.
In HR settings, overt behavior is often used during performance reviews because it reflects how employees act in real situations.
Managers rely on overt behavior to evaluate professionalism, teamwork, and compliance with company rules.
Since this behavior is outward, it is usually influenced by workplace expectations, leadership style, and organizational culture.
Examples include speaking during meetings, following office policies, arriving on time, or completing assigned tasks.
2. Covert Behavior
Covert behavior refers to internal actions that are not visible to others. This includes thoughts, emotions, beliefs, and internal stress responses.
While covert behavior cannot be directly observed, it strongly influences how a person behaves outwardly.
In the workplace, covert behavior may include anxiety before a presentation, frustration over workload, or motivation to achieve goals.
In the workplace, HR professionals often consider covert behavior when addressing employee well-being, engagement, and job satisfaction.
Tools such as surveys, feedback sessions, and one-on-one discussions help identify covert behavior patterns that may affect performance.
3. Voluntary Behavior
Voluntary behavior involves actions that are taken by choice. These behaviors are intentional and usually guided by thinking, planning, and decision-making.
In HR contexts, voluntary behavior reflects initiative, accountability, and work ethics. Employees showing positive voluntary behavior often adapt well to change and learning opportunities.
HR teams encourage this type of behavior through clear goals, recognition, and growth opportunities, as it supports long-term organizational success.
Examples include choosing to collaborate with a team, solving a problem independently, or volunteering for additional responsibilities.
4. Involuntary Behavior
Involuntary behavior occurs automatically and without conscious control. These behaviors are often quick responses to emotional or physical triggers.
At work, involuntary behavior may appear during high-pressure situations such as tight deadlines or conflict.
While this behavior is natural, repeated involuntary reactions can affect communication and performance.
HR teams address involuntary behavior by promoting stress management practices, emotional awareness, and supportive work environments.
Examples include sudden reactions to stress, nervous habits, or instinctive responses under pressure.
10 Types of Human Behavior
Human behavior shows up in many ways at work and in daily interactions. These types of behavior help HR teams understand how employees communicate, respond to situations, and work with others.
1. Aggressive Behavior
Aggressive behavior shows when a person reacts strongly and forcefully toward others.
A person with this behavior may raise their voice, argue often, interrupt people, or react badly to feedback.
They may blame coworkers instead of taking responsibility and may become angry during disagreements.
Common traits include impatience, poor anger control, and difficulty accepting opinions that differ from their own.
At work, aggressive behavior can create fear, stress, and tension among team members. HR teams usually step in early to prevent conflict and protect a respectful work environment.
2. Assertive Behavior
Assertive behavior means expressing thoughts and needs in a calm and respectful way.
A person with this behavior speaks clearly, listens to others, and shares opinions without being rude or demanding.
They are comfortable asking questions, setting boundaries, and explaining concerns.
People with assertive behavior show confidence, self-control, and fairness. In the workplace, this behavior helps with teamwork, leadership, and problem-solving.
HR professionals often encourage assertive behavior because it supports healthy communication and mutual respect.
3. Passive Behavior
Passive behavior appears when a person avoids conflict or stays silent even when their input matters.
Someone with this behavior may say “yes” even when they disagree, avoid speaking in meetings, or delay decisions out of fear of upsetting others.
Common traits include low confidence, fear of disagreement, and difficulty expressing needs.
Over time, passive behavior may lead to frustration, low job satisfaction, and reduced performance.
HR teams often support these employees through communication training and regular feedback.
4. Cooperative Behavior
Cooperative behavior focuses on working together and supporting shared goals.
A person with this behavior listens carefully, helps teammates, and is willing to share tasks and responsibilities. They respect different opinions and aim for group success.
Traits include teamwork, patience, and reliability. Cooperative behavior improves trust and efficiency in the workplace.
HR departments value this behavior because it strengthens collaboration and builds a positive work culture.
5. Competitive Behavior
Competitive behavior is driven by goals, results, and achievement. A person with this behavior works hard to meet targets, improve performance, and gain recognition.
They often enjoy challenges and like measuring progress through results.
Traits include ambition, focus, and motivation. When managed well, competitive behavior can improve productivity. When unchecked, it may cause stress or harm to teamwork.
HR policies often help balance competition so it remains fair and healthy.
6. Social Behavior
Social behavior reflects how a person interacts with others in group settings.
Someone with strong social behavior communicates openly, joins discussions, and builds relationships at work. They often feel comfortable engaging with colleagues across teams.
Traits include friendliness, communication skills, and emotional awareness. Social behavior supports trust, teamwork, and employee engagement.
HR teams rely on social behavior to strengthen workplace connections and morale.
7. Antisocial Behavior
Antisocial behavior involves actions that ignore workplace rules or social expectations.
A person with this behavior may show little respect for policies, avoid teamwork, or act without considering how their actions affect others.
Traits include poor cooperation, lack of accountability, and resistance to structure. Antisocial behavior can disrupt teams and lower morale.
HR professionals manage this behavior through clear rules, documentation, and corrective steps.
8. Emotional Behavior
Emotional behavior is guided by feelings rather than careful thinking.
A person with this behavior may react strongly to stress, feedback, or change. Their mood can affect how they speak, decide, and work with others.
Traits include emotional sensitivity and quick reactions. Emotional behavior is natural, but when unmanaged, it may affect performance.
HR teams often support emotional balance through wellness programs and supportive management practices.
9. Habitual Behavior
Habitual behavior includes actions repeated regularly over time.
A person with this behavior follows routines without much thought, such as arriving on time, responding to emails in a certain way, or handling tasks consistently.
Traits include consistency and predictability. Positive habits support reliability, while negative habits may limit improvement.
HR professionals focus on shaping habits through training, feedback, and workplace standards.
10. Learned Behavior
Learned behavior develops through experience, training, and observation.
A person with this behavior adjusts actions based on feedback, rules, and workplace learning. Their behavior improves as they gain knowledge and skills.
Traits include adaptability, openness to feedback, and willingness to improve. Learned behavior shows that behavior can change over time.
HR teams depend on training and development programs to support positive learned behavior.
Tip for FreshersFor freshers, adding types of behavior along with core skills can strengthen a CV. Behavior highlights work habits and attitude, while skills reflect technical and practical ability. Those looking for skill examples may refer to 50+ Different Types of Skills to Learn for additional clarity. |
Types of Behavior to Mention in a CV
Types of behavior listed on a CV help employers understand how a candidate works, communicates, and handles responsibility. These behaviors focus on actions and work habits rather than personality traits.
| Behavior Type | How to Describe It in Your CV |
|---|---|
| Professional Behavior |
|
| Leadership Behavior |
|
| Team-Oriented Behavior |
|
| Ethical Behavior |
|
| Adaptive Behavior |
|
| Responsible Behavior |
|
| Positive Work Behavior |
|
| Organized Behavior |
|
| Assertive Behavior |
|
| Cooperative Behavior |
|
Are Behavior and Nature the same?
Behavior refers to how a person acts in different situations.
It includes actions, reactions, communication style, and work habits. Behavior can change over time through learning, experience, feedback, and environment.
Nature refers to the inborn traits a person is born with. This includes natural tendencies such as temperament, emotional sensitivity, or basic personality traits.
Nature is more stable and less influenced by training or workplace rules.
In simple terms, nature is what a person is born with, while behavior is how a person chooses to act in daily and professional life.
HR teams focus more on behavior because it can be observed, guided, and improved.
Also, nature stays largely the same, while behavior can improve, adjust, or shift. This is why HR teams focus more on behavior, since it can be shaped through guidance, policies, and development support.
Conclusion
Understanding different types of behavior helps organizations manage people more effectively.
From psychology-based behavior to everyday workplace actions, behavior influences communication, teamwork, and performance.
HR teams often use behavior patterns to support hiring decisions, employee development, and conflict management.
For job seekers, especially freshers, listing relevant types of behavior on a CV helps employers see work habits, attitude, and readiness beyond skills alone.
When behavior and skills are presented together, they offer a clearer picture of how a person works in real situations.
Thoughts or observations about workplace behavior can be shared in the comments to continue the discussion and support practical learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Type Of Behavior Is Stress?
Stress is an emotional and psychological behavior that affects reactions, focus, and communication. In workplaces, unmanaged stress can influence performance, decision-making, and employee well-being.
Why Are Types Of Behavior Important In The Workplace?
Types of behavior help HR teams understand employee actions, communication styles, and responses to pressure, supporting better hiring, performance reviews, and workplace management.
Can Behavior Change Over Time?
Yes, behavior can change through learning, experience, feedback, and training. Workplace policies and development programs often influence positive behavior change over time.